discover the fused cast refractories product range
At Motim, we understand that having a variety of casting methods and materials is essential to meet the diverse needs of our customers. That's why we offer a wide selection for you to choose from, ensuring that you can find the perfect fit for your project. Whether you require the best quality materials for high temperature zones or more cost efficient ones for low exposure zones, we have you covered. With our range of options, you can select the method and material that aligns best with your specifications, guaranteeing high-quality results every time.
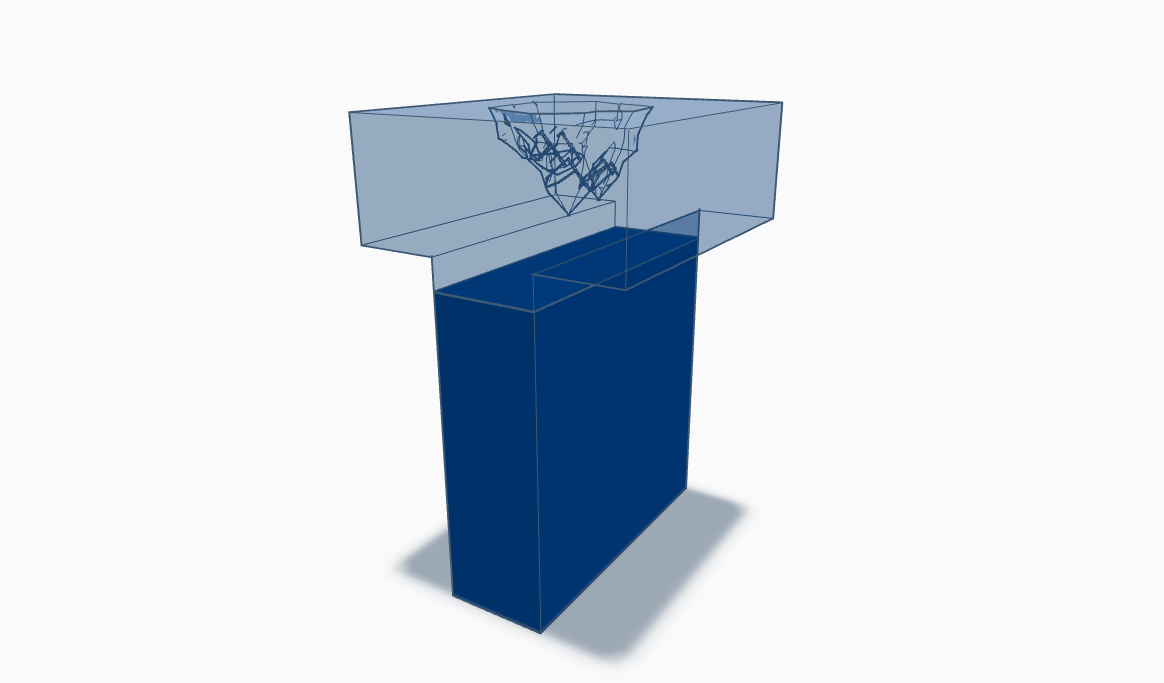
MOTIM carefully manages shrinkage cavities in fused cast refractory production to enhance block performance against wear. Korvisit and Zirkosit blocks are manufactured with various casting methods, offering solutions with reduced cavities. Non-destructive testing monitors cavity location and block solidity. A computer program compares radiation intensity values to determine block solidity, documented alongside cavity location according to quality standards.
our casting methods
-
Type: N
The shrinkage cavity is located in the middle of the side, opposite to the working face near to the surface.
-
Type: EL
The casting is made from the end of the block opposite to the metal line and the major shrinkage cavity is cut off.
-
Type: KLB/KLP/KLS
The part of the block containing the shrinkage cavity is cut off.
Materials and production methods
MOTIM introduced the original α-corundum type fused cast refractory in 1957. KORVISIT-AB is similar to KORVISIT-A, but features an αβ type crystal structure, ideal for lower temperature zones in glass melting furnaces. To meet the demands of modern high-capacity furnaces, MOTIM introduced AZS type fused cast refractory blocks in 1965, marketed under the name ZIRKOSIT. These blocks, containing α-corundum and baddeleyite, offer outstanding performance in low and high temperature applications, while silica and low alkali content enhance thermal shock resistance. Since 1986, ZIRKOSIT products are supplied in oxidized form, and MOTIM now offers three types of AZS refractories, allowing customers to select the most economical solution for their furnaces.
ZIRKOSIT-S32
32,6% zirconium-dioxide content
excellent result both in high and low temperature zones
long history of use in glass melting furnaces
recommended for:
Casting methods:
-
Recommended use: superstructure, working end, feeder channels and non-glass-contact-areas
-
Recommended use: superstructure, working end and feeder channels
-
Recommended use: bottom paving, side wall patching and joint cover blocks
ZIRKOSIT-M36
36,2% zirconium-dioxide content
better performance than S32 but more economical than Y41
recommended for:
side walls
superstructures
working ends
bottom paving
feeder channels
Casting methods:
-
Recommended use: superstructure, working end and feeder channels
-
Recommended use: side walls
-
Recommended use: side walls, corner blocks, bubbling blocks and weir blocks
-
Recommended use: bottom paving
-
Recommended use: bottom paving, side walls, superstructure and feeder channels
ZIRKOSIT-y41
41% zirconium-dioxide content
our highest zirconium-dioxide content AZS type fused cast refractory material
yields excellent results in most exposed parts of the glass melting furnace
recommended for:
weir
throat
side walls
corner blocks
electrode blocks
bubbling blocks
Casting methods:
-
Recommended use: superstructure, working end and feeder channels
-
Recommended use: side walls
-
Recommended use: throat, doghouse corner, side wall blocks, electrode blocks, bubbling blocks and weir blocks
-
Recommended use: bottom paving and patching tiles
-
Recommended use: doghouse, thoat, weir, bubbling blocks and electrode blocks
Korivisit-A
reputed refractory and wear resistant lining of reheating furnaces
resistant to mechanical wear in high temperature conditions
recommended for:
skid rails
soaking zone bottom of heavy duty pusher-type furnaces reheating ingots
lining exit chutes in walking beam furnaces
Casting methods:
Korvisit-A N
Korivisit-AB
Alpha-Beta-type fused cast refractory material
superior corrosion resistance and low blister potential
ideal product for the lower temperature zones of the glass melting furnaces
recommended for:
side walls
bottom paving of working ends
feeder channels
certain parts of superstructures
drawing chambers of sheet glass furnaces
Casting methods:
-
Recommended use: side walls, bottom paving of working ends, feeder channels, certain parts of the superstructure
-
Recommended use: side walls bottom paving of working ends, feeder channels, drawing chambers of sheet glass furnaces and superstructures (from the 4th burner port)
-
Recommended use: bottom paving
Korivisit-B
Beta-Alumina-type fused cast refractory material
very strong resistance to alkaline vapor and thermal shock at elevated temperature
recommended for:
superstructures
Casting methods:
-
Recommended use: superstructures
-
Recommended use: superstructures
Together with our fused cast refractory blocks, we also provide unshaped refractories. For the bedding mixes below the paving we use hydraulic bond monolithic mixes called ZIRMOTIM and ALMOTIM. Both of our products are available in different grain sizes ranging from up to 5 mm to 0.5 mm. Such bedding mixes act as leveling courses to ensure a stable setting for the blocks and reduces the possiblity of glass penetration.
unshaped refractories
Almotim
AMOTIM concretes are made out of fused alumina grains
we offer it in combination with Korvisit fused cast alumina shapes in the working end and feeder channels
Recommended use:
ALMOTIM-5 used directly on the subpaving
ALMOTIM-2 is the bedding layer for fused cast tiles and feeder shapes
zirmotim
made out of fused AZS grains
applied with the bottom paving tiles
acts as safety layer minimizin glass infiltration
helps prevent glass flow under the tiles
the different types have same chemical composition but varying grain size
Recommended use:
ZIRMOTIM-5 used directly on the subpaving
ZIRMOTIM-2 is the bedding layer for fused cast tiles
ZIRMOTIM-0,5 for filling the residual joints
hot repair mixes
chemically bonded
can be applied as a separation course between silica based materials and AZS type materials
for hot-repair of silica based materials